NASA engineers working on competing plan for moon rocket
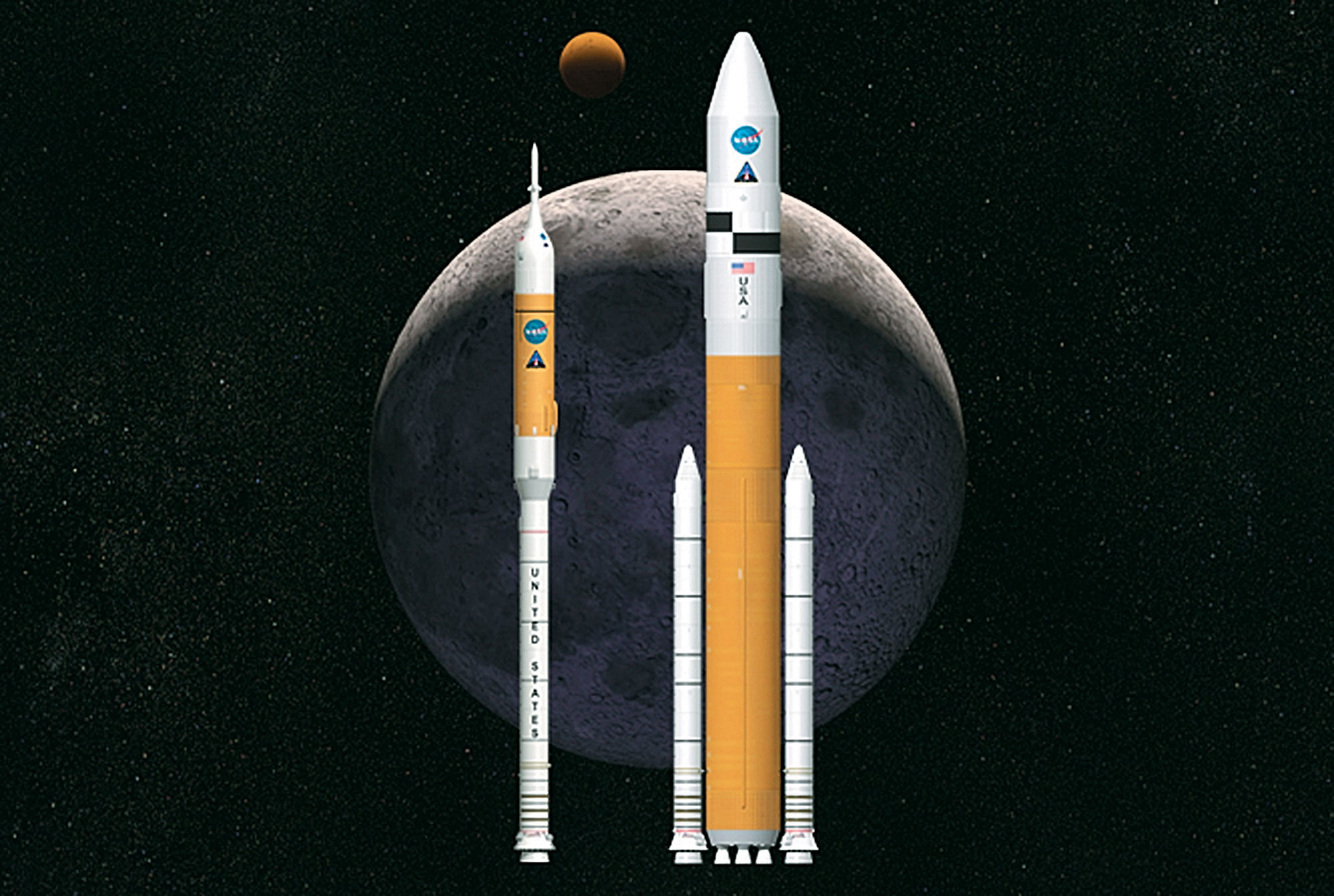

This artist's rendering shows NASA's next generation of moon rockets being developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. Ares I, at left, is the crew-launch vehicle that will carry astronauts to space. Ares V is the cargo launch vehicle that will deliver the lunar lander and other large hardware to space.
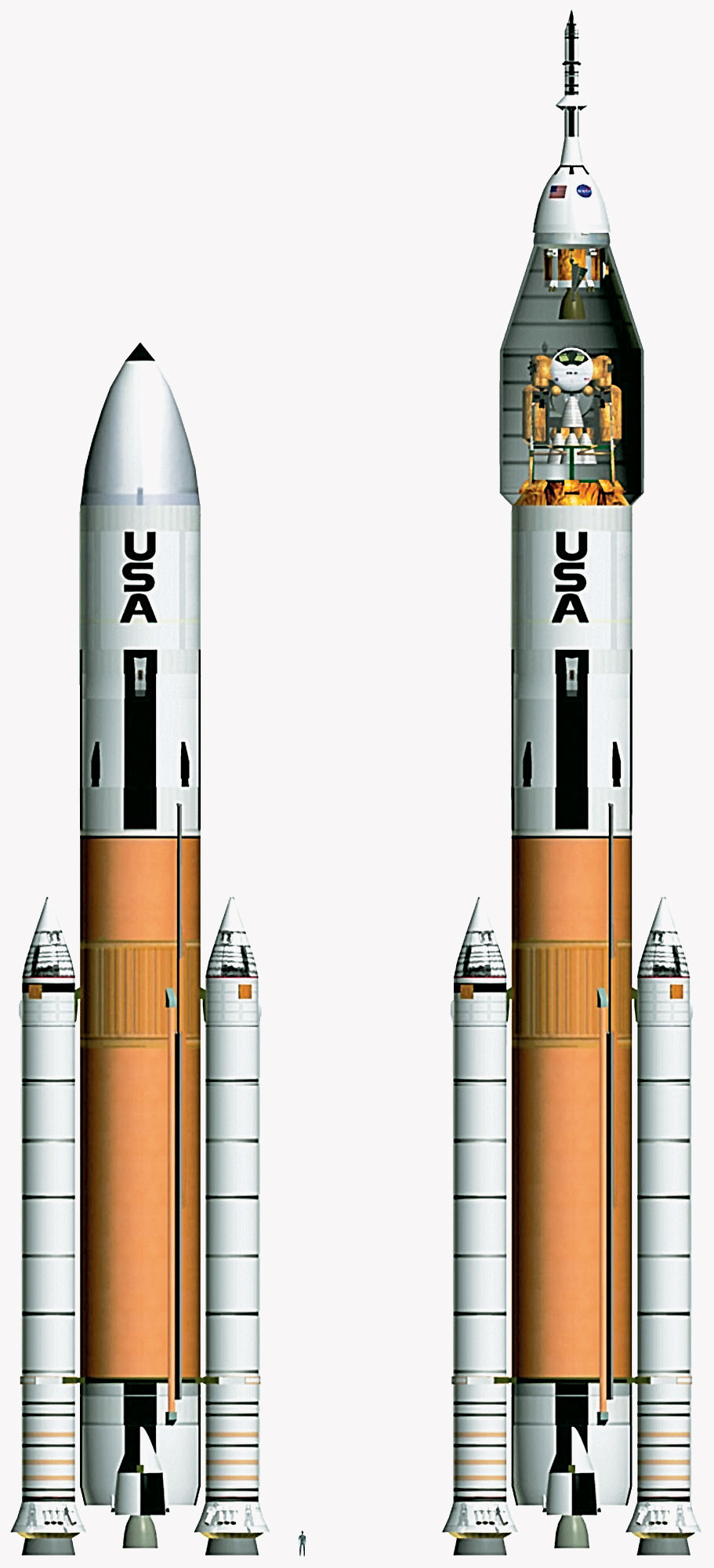
This rendering released by Direct Launcher shows a rocket design that advocates say is a better alternative for returning to the moon than the Ares rockets being built by NASA. The Jupiter 232 rocket on the left would be used for cargo launches, while the version of the right could launch both cargo and astronauts. NASA engineers are among those working on the competing design.
Huntsville, Ala. ? By day, the engineers work on NASA’s new Ares moon rockets. By night, some go undercover to work on a competing design.
These dissenting scientists and their backers insist they have created an alternative rocket that would be safer, cheaper and easier to build than the two Ares spacecraft that will replace the space shuttle.
They call their project Jupiter, and like Ares, it’s a brainchild of workers at the Marshall Space Flight Center and other NASA facilities. The engineers involved are doing the work on their own time and mostly anonymously, with the help of retirees and other space enthusiasts.
A key Ares project manager dismisses their design as little more than a sketch on a napkin that won’t work.
A spokesman for the competing effort, Ross Tierney, said concerned engineers at NASA and some contractors want a review of the Ares plans but can’t speak out for fear of being demoted, transferred or fired.
The Jupiter design is being reviewed by a team of 57 volunteer engineers, from line engineers up to NASA middle managers, Tierney said. Those numbers are dwarfed by NASA’s Ares work force, which has thousands of government workers and contractors.
The head of the Ares office at Marshall said he can’t rule out the possibility that some of his people are involved with the underground program.
“I don’t know what people do on their own time,” Steve Cook said in a recent interview with The Associated Press.
But Cook said he is familiar with the Jupiter project, and he’s not impressed. NASA informally reviewed plans for the rocket and determined the idea to be a flawed scheme based on shaky numbers.
“It’s not feasible. We said, ‘It doesn’t work’ and moved on,” Cook said.
Meanwhile, he said, work on the Ares I rocket is so far along that the first test flight is less than a year away.
“We’re down to the nuts and bolts : on this rocket. This is not a napkin drawing,” he said.
The debate reflects disagreement over the direction of U.S. spaceflight as NASA prepares to retire the shuttle in 2010. By 2015, the agency plans to begin orbital flights with Ares I and a companion heavy-lift cargo rocket, Ares V. Officials hope to return astronauts to the moon by 2020.
Astronauts will ride into orbit in a capsule aboard the Ares I, which will have a modified shuttle booster rocket at its core. They will dock with a lunar stage that was carried aloft separately by an Ares V rocket and head to the moon.
The Jupiter design would also require two separate launches to get to the moon, but its rockets would both rely on a shuttle external tank at their center. Some of the design concepts go back to proposals floated at Marshall in the early 1980s.
Besides being a simpler, more powerful system, backers say, the Jupiter rockets would save NASA $19 billion in development costs and another $16 billion in operating costs over two decades.
The Government Accountability Office last year raised questions about the cost of NASA’s plan for returning to the moon, which a report estimated at $230 billion over 20 years. NASA said it already has spent about
$7 billion on Ares.
Steve Metschan, an engineer and former NASA contractor who supports the Jupiter team, accused NASA of suppressing information that shows Jupiter would perform better than Ares.
Cook said all the estimates on Jupiter were preliminary, and he denied critics’ claims that NASA did a full-fledged study of the Jupiter rocket or the engineers’ alternate moon-mission program, which they call Direct 2.0.







